By: Rozhin Yasaei (UC Irvine), Sina Faezi (UC Irvine), and Mohammad Abdullah Al Faruque (UC Irvine)
Stage: IC Fabrication
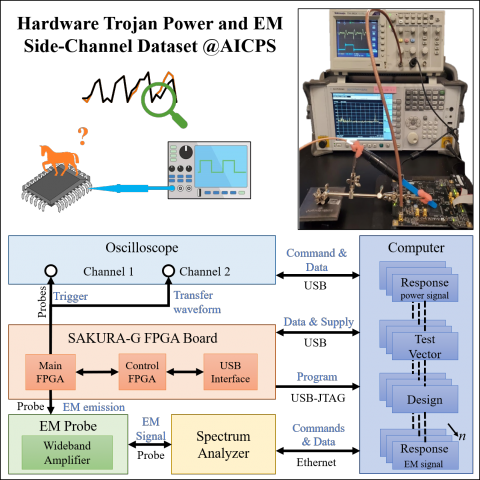
Summary
Design and fabrication outsourcing has made integrated circuits vulnerable to malicious modifications by third parties known as hardware Trojan (HT). Over the last decade, the use of side-channel measurements for detecting the malicious manipulation of the chip has been extensively studied. However, the suggested approaches mostly suffer from two major limitations: reliance on trusted identical chip (e.i. golden chip); untraceable footprints of subtle hardware Trojans which remain inactive during the testing phase. To overcome these shortcomings, we propose a novel idea of maintaining a dynamic model of the integrated circuit throughout its life cycle for the purpose of detecting HT that might have been injected anywhere in the supply chain. In this paper, we gather a comprehensive dataset of power and Electromagnetic (EM) side-channel signals for hardware Trojan benchmarks from Trust Hub benchmarks to develop a statistical model of the chip for HT detection. To be used in a golden chip-free Trojan detection approach, the side-channel data is collected in the presence of HT under two scenarios: when the HT is inactive and when it is activated. Consequently, all the measured power data include the static power of HT in addition to base circuit power consumption, which makes the detection more challenging. The only difference between the two data collection scenarios is the dynamic power consumption of HT.
Contact
Input/Output Interface
- Input: none
- Output: .csv
Dependencies
The dataset manual
Licensing Info
Creative Commons Attribution (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
References
Brain-Inspired Golden Chip Free Hardware Trojan Detection Journal Article
In: IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, vol. 16, pp. 2697–2708, 2021.
Acknowledgments
- University of California Irvine, This research was supported by the Office of Naval Research (ONR) award N00014-17-1-2499.